ASTM A334 tubes are carbon and alloy steel tubes designed for low-temperature applications and manufactured using seamless and welded processes.
Some product sizes may not be available under this specification because heavier wall thicknesses have an adverse effect on low-temperature impact properties.

Grade Classification
ASTM A334 contains several grades for different low-temperature environments.
Grade 1, Grade 3, Grade 6, Grade 7, Grade 8, Grade 9, and Grade 11.
The corresponding grades for alloy steel tubes are Grade 3, Grade 7, Grade 8, Grade 9, and Grade 11.
Each grade of steel has its own specific chemical composition and mechanical property requirements, as well as minimum impact test temperature criteria that must be met.
Manufacturing Processes
The tubes shall be made by the seamless or automatic welding process with no addition of filler metal in the welding operation.
Heat Treatment
Grade 1, 3, 6, 7, and 9
Normalize by heating to a uniform temperature of not less than 1550 °F [845 °C] and cool in the air or in the cooling chamber of an atmosphere-controlled furnace.
If tempering is required, it will need to be negotiated.
For the above grades of seamless steel tubes only:
Reheat and control hot working and the temperature of the hot-finishing operation to a finishing temperature range from 1550 - 1750 °F [845 - 955℃] and cool in a controlled atmosphere furnace from an initial temperature of not less than 1550 °F [845 °C].
Grade 8
Select any of the following methods for heat treatment.
Quenched and Tempered;
Double Normalized and Tempered.
Grade 11
Whether to anneal Grade 11 tubes is per agreement between purchaser and supplier.
When Grade 11 tubes are annealed they shall be normalized in the range of 1400 - 1600℉[760 - 870 °C].
ASTM A334 Chemical Composition
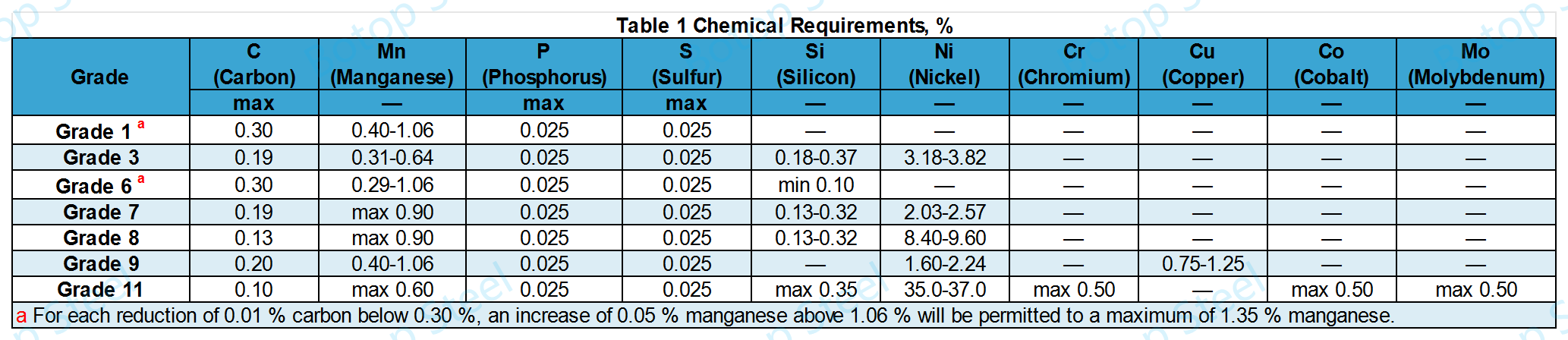
For Grade 1 or Grade 6 steels, it is not permitted to provide alloying grades for any elements other than those expressly required. However, it is permitted to add elements necessary for the deoxidation of the steel.
ASTM A334 Mechanical Tests
Mechanical property requirements do not apply to tubing smaller than 1/8 in. [3.2 mm] in outside diameter and with a wall thickness under 0.015 in. [0.4 mm].
1. Tensile Property
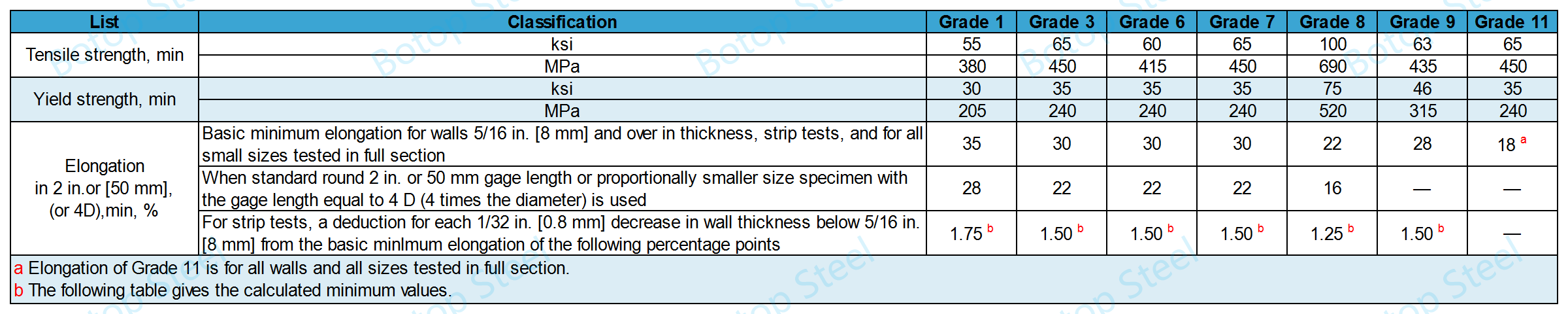
Minimum elongation calculated for each 1/32 inch [0.80 mm] reduction in wall thickness:
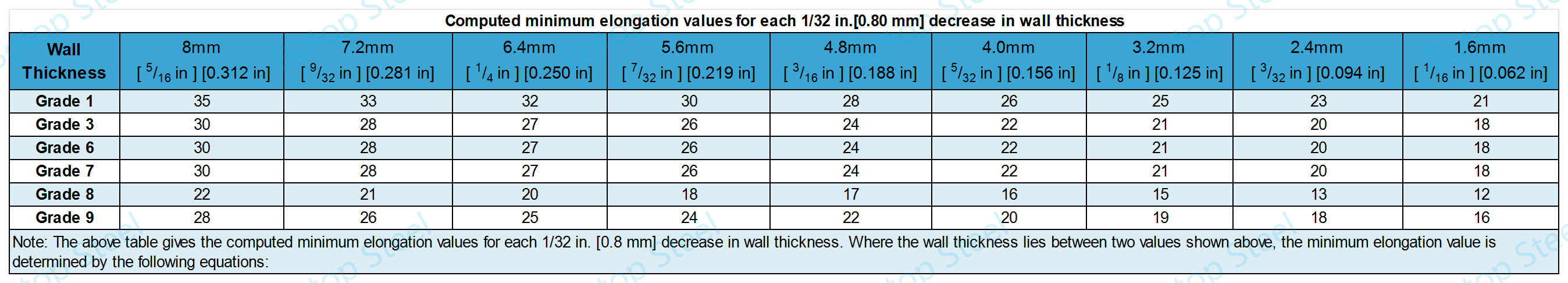
For tubing smaller than 1/2 in. [12.7 mm] in outside diameter, the elongation values given for strip specimens shall apply.
2. Impact Tests
Select the appropriate temperature and corresponding impact strength based on grade and wall thickness.
Impact Strength
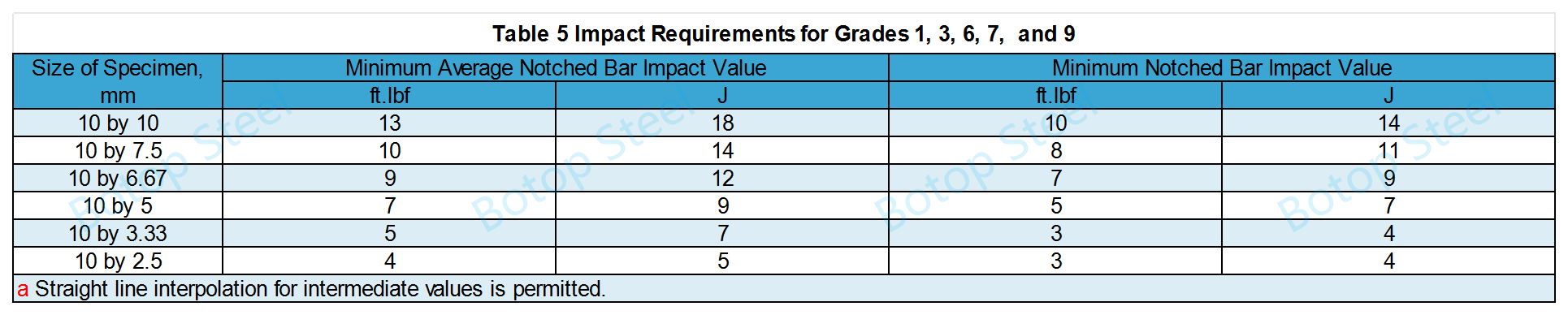
Impact Temperature
| Grade | Impact Test Temperature | |
| ℉ | ℃ | |
| Grade 1 | -50 | -45 |
| Grade 3 | -150 | -100 |
| Grade 6 | -50 | -45 |
| Grade 7 | -100 | -75 |
| Grade 8 | -320 | -195 |
| Grade 9 | -100 | -75 |
3. Hardness Test
| Grade | Rockwell | Brinell |
| Grade 1 | B 85 | 163 |
| Grade 3 | B 90 | 190 |
| Grade 6 | B 90 | 190 |
| Grade 7 | B 90 | 190 |
| Grade 8 | — | — |
| Grade 11 | B 90 | 190 |
4. Flattening Test
One flattening test shall be made on specimens from each end of one finished tube of each lot but not the one used for the flare or flange test.
5. Flare Test (Seamless Tubes)
One flare test shall be made on specimens from each end of one finished tube of each lot, but not the one used for the flattening test.
6. Flange Test (Welded Tubes)
One flange test shall be made on specimens from each end of one finished tube of each lot, but not the one used for the flattening test.
7. Reverse Flattening Test
For welded tubes, one reverse flattening test shall be made on a specimen from each 1500 ft [460 m] of finished tubing.
Hydrostatic or Nondestructive Electric Test
Each pipe shall be nondestructively electrically tested or hydrostatically tested in accordance with Specification A1016/A1016M.
Applications for ASTM A334 Steel Pipe
Primarily used to transport fluids or gases such as natural gas, oil, and other chemicals at low temperatures.
1. Cryogenic piping systems: commonly used in the construction of piping systems for the transportation of cryogenic fluids (e.g. liquefied natural gas, liquid nitrogen). Due to its excellent cryogenic properties, it is able to maintain mechanical strength and toughness at very low temperatures.
2. Heat exchangers and condensers: Heat exchangers and condensers can be effectively used to cool or heat process media, especially in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
3. Pressure vessels: may also be used to manufacture pressure vessels designed for cryogenic operations. These vessels may be used to store cryogenic chemicals or for specialized industrial processes.
4. Refrigeration systems and equipment: These tubes are used for the transportation of refrigerants, especially where low-temperature-resistant materials are required.
ASTM A334 Equivalent Standard
EN 10216-4: Covers non-alloyed and alloyed steel tubes, which have specified low-temperature properties.
JIS G 3460: relates to alloy steel tubes for cryogenic service.
GB/T 18984: applies to seamless steel tubes for cryogenic pressure vessels. It specifies in detail the design and manufacture of steel tubes suitable for extreme low-temperature environments.
While these standards may differ in details and specific requirements, they are similar in their overall objective and application, which is to ensure the safety and performance of steel pipes in cryogenic environments.
Our Related Products
Since its establishment in 2014, Botop Steel has become a leading supplier of carbon steel pipe in Northern China, known for excellent service, high-quality products, and comprehensive solutions.
The company offers a variety of carbon steel pipes and related products, including seamless, ERW, LSAW, and SSAW steel pipe, as well as a complete lineup of pipe fittings and flanges. Its specialty products also include high-grade alloys and austenitic stainless steels, tailored to meet the demands of various pipeline projects.
Tags: ASTM A334, carbon steel pipe, astm a334 gr 6, astm a334 gr 1.
Post time: May-20-2024
